[Research Report] Public Opinion Survey on COVID-19 Vaccines and Immunization and Vaccination Policy (June 17, 2022)
date : 6/17/2022
![[Research Report] Public Opinion Survey on COVID-19 Vaccines and Immunization and Vaccination Policy (June 17, 2022)](https://hgpi.org/en/wp-content/uploads/sites/2/vaccine-survey-202206-top_ENG.jpg)
Health and Global Policy Institute (HGPI) has presented the results of a public opinion survey on COVID-19 vaccines and immunization and vaccination policy.
The survey was conducted on March, 2022 among 1,000 people selected by region, age, and sex in ratios in that correspond to the demographics of the total population of Japan.
In addition to opinions regarding COVID-19 vaccines, the survey also examined general topics in immunization and vaccination policy.
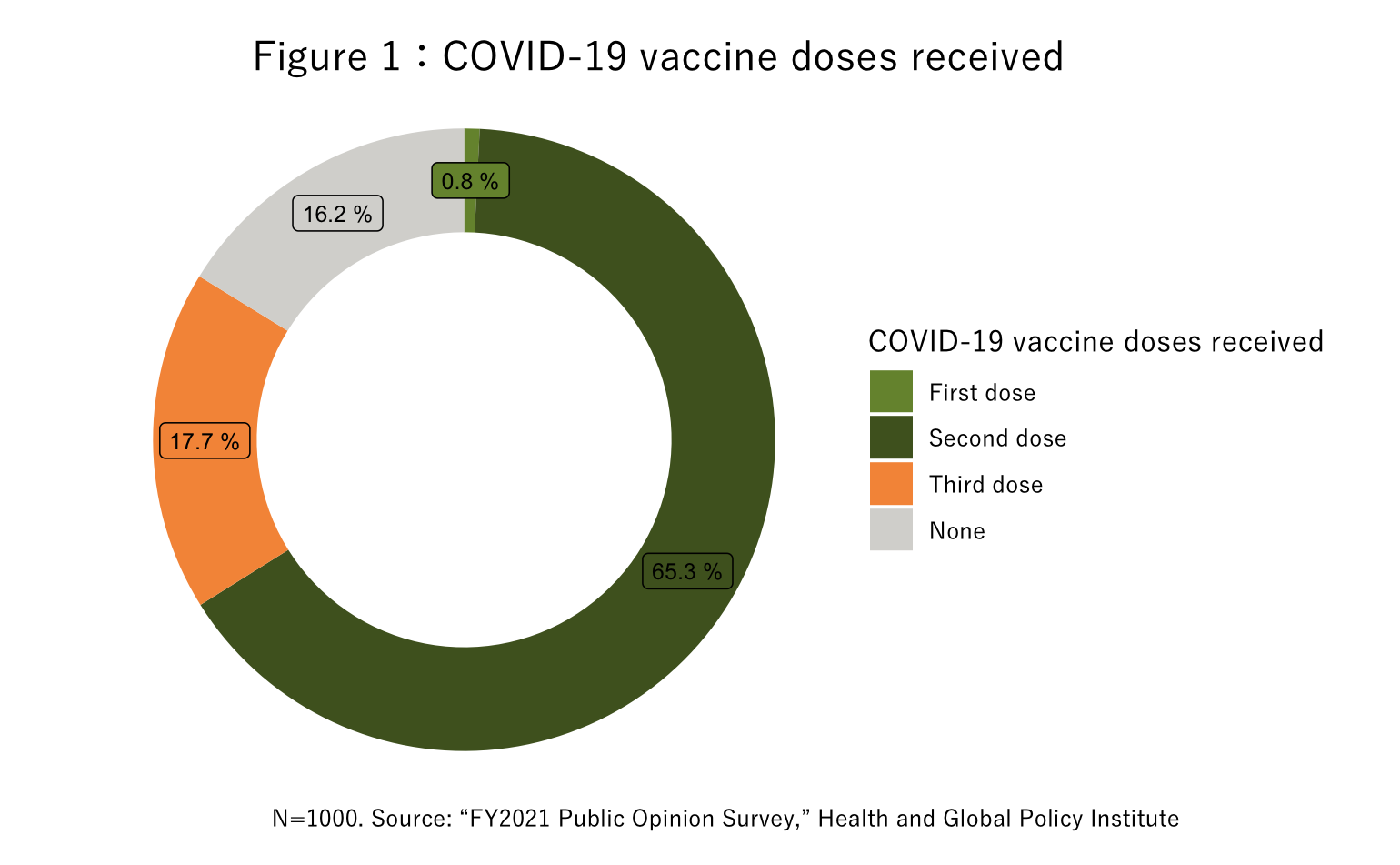
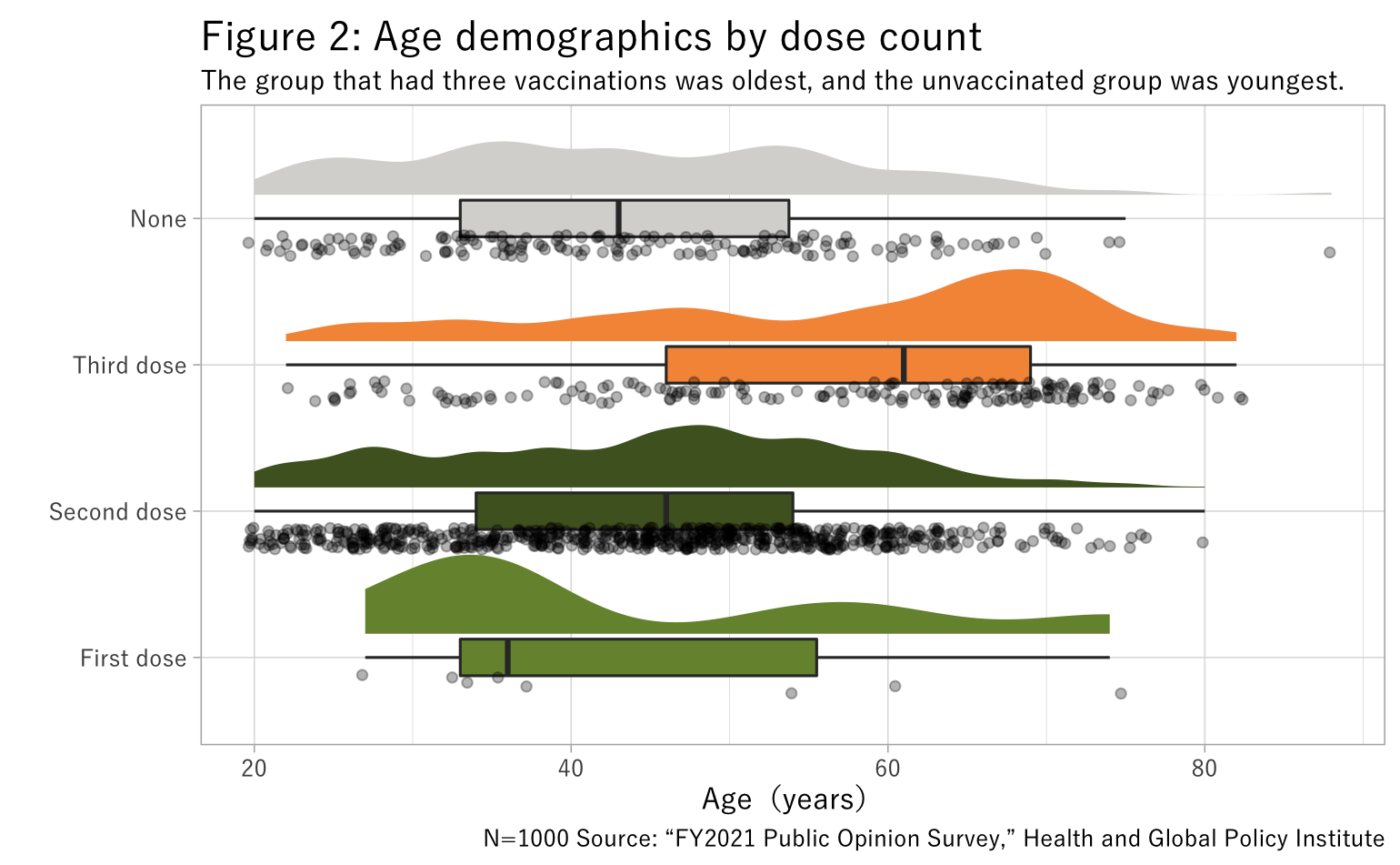
Figures 1 and 2 show COVID-19 vaccination status among respondents when the survey was conducted.
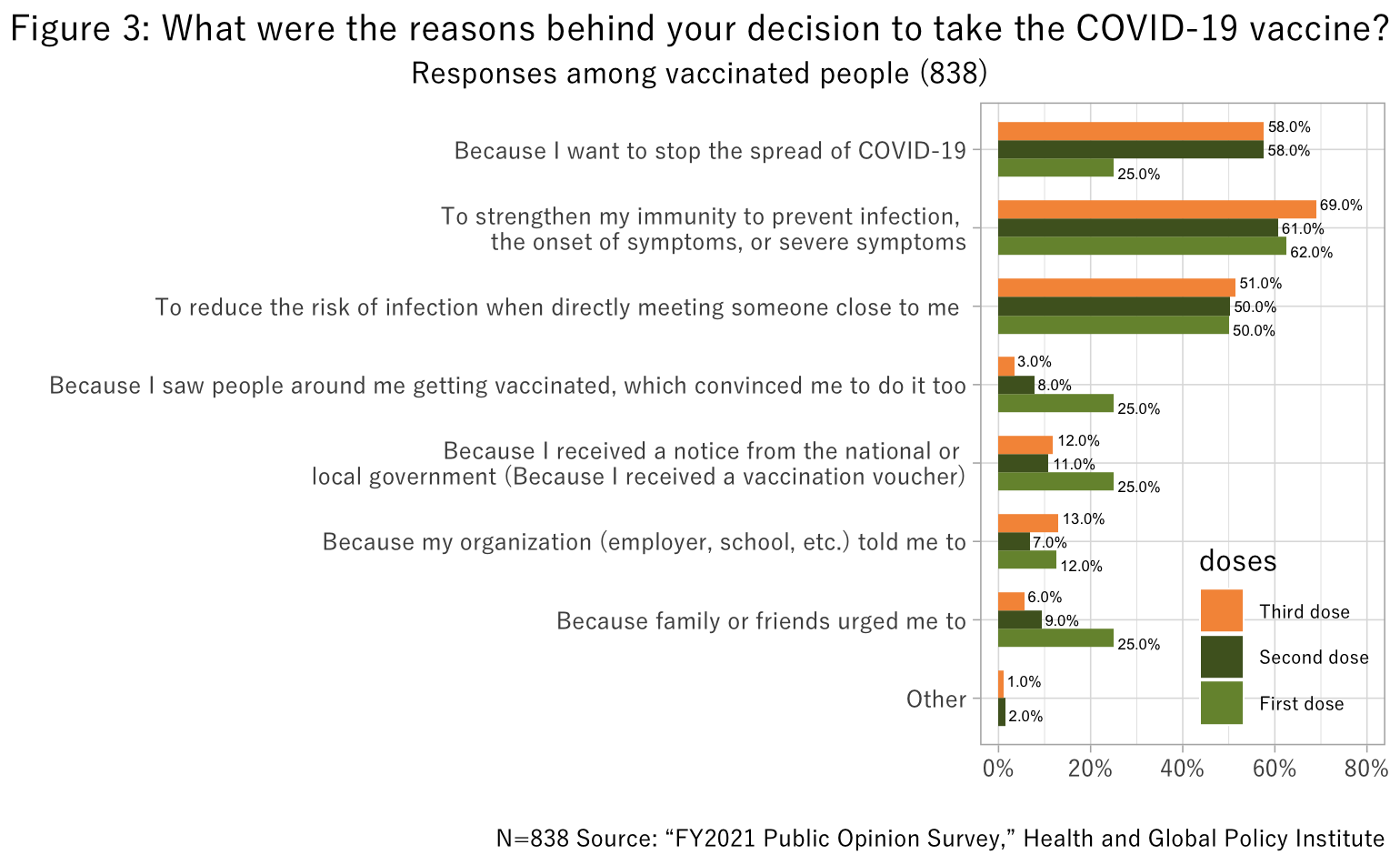
Reasons for taking COVID-19 vaccines are as shown below. Over half of respondents who took the second and third doses said they decided to get vaccinated to more effectively help contain the pandemic; to prevent infection, the onset of symptoms, and the development of severe symptoms; as well as to reduce the risk of infections when coming into contact with people close to them (Figure 3).
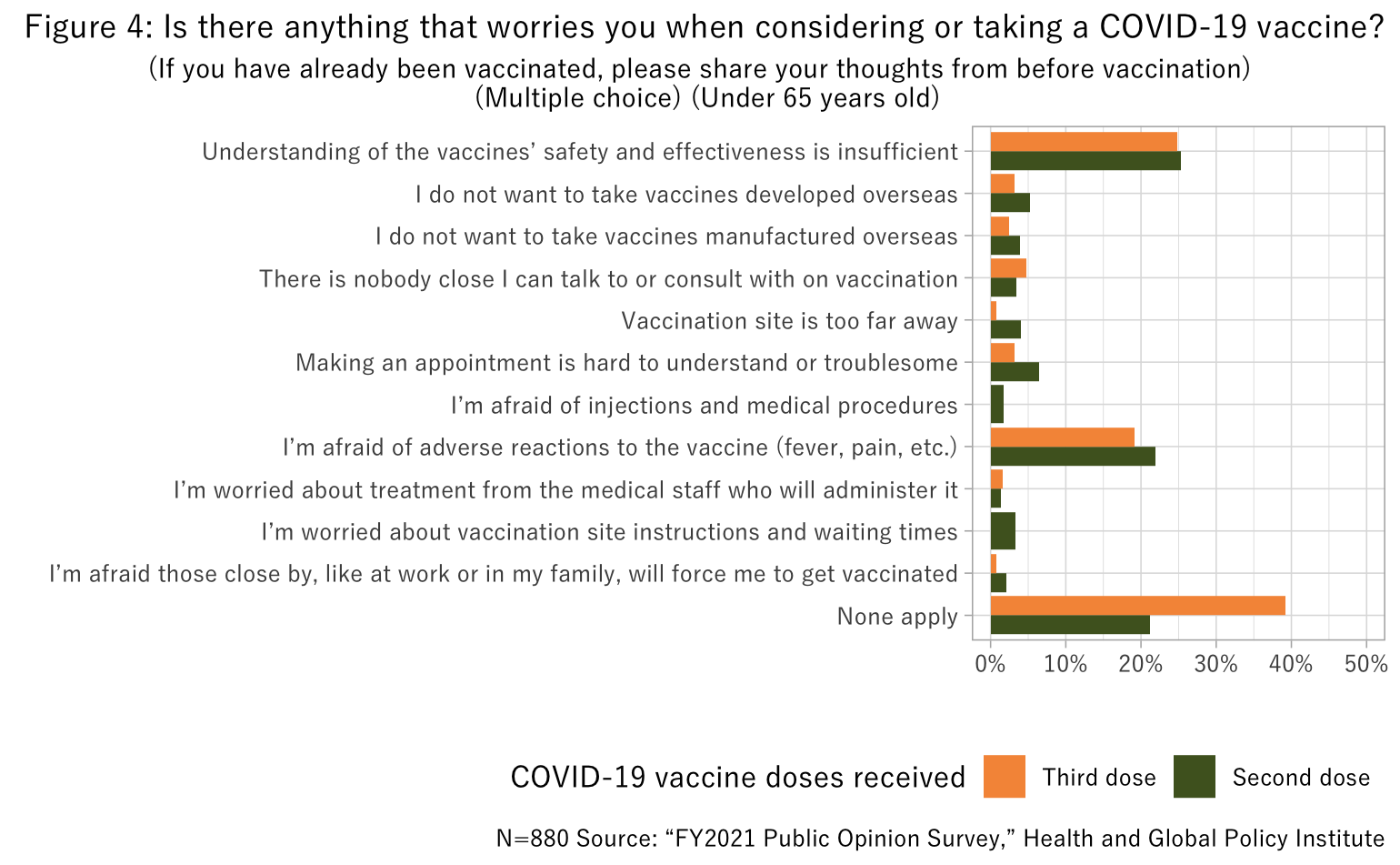
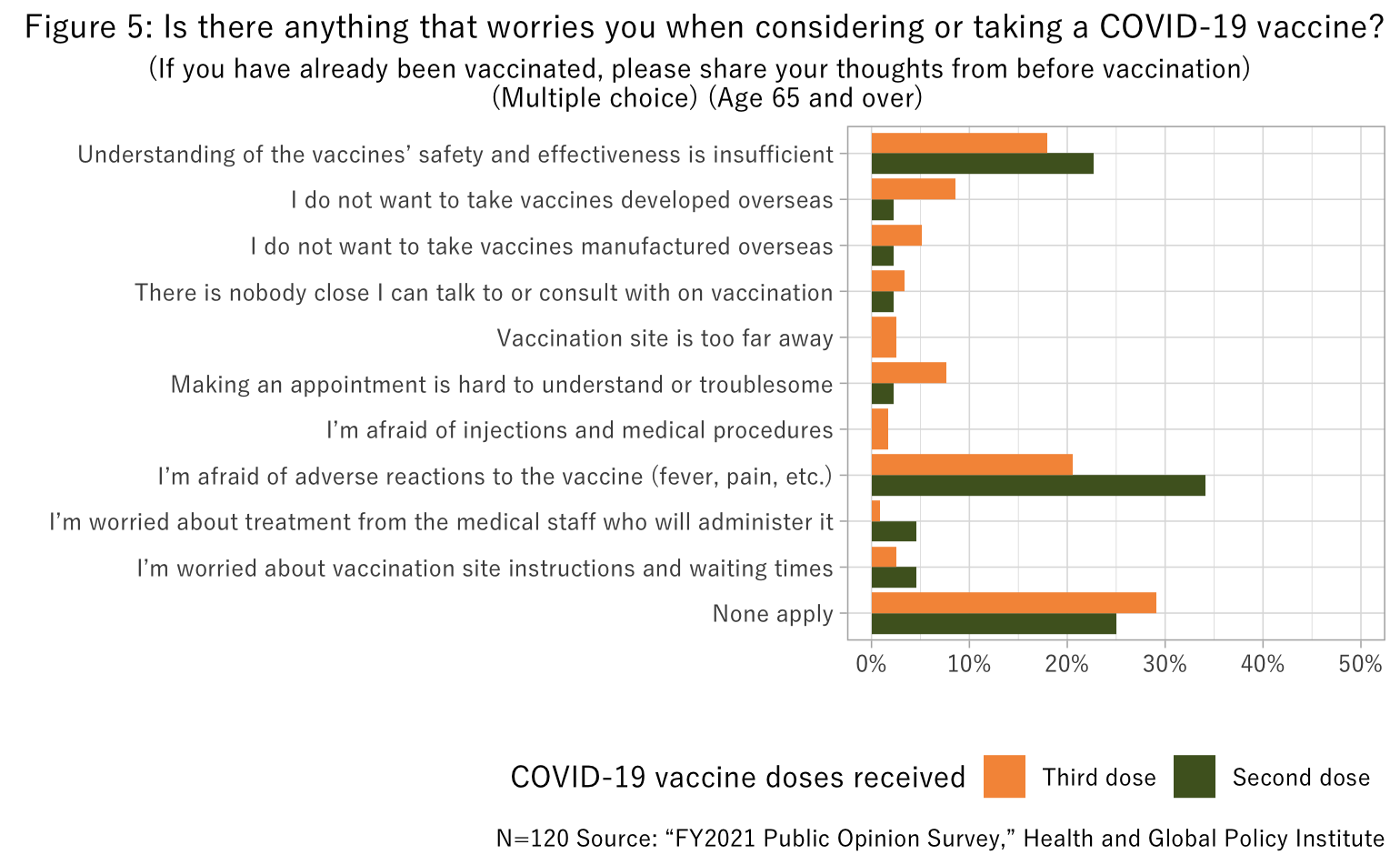
On the other hand, when considering taking COVID-19 vaccines, concerns about adverse reactions and vaccine effectiveness and safety were seen among both respondents under age 65 and respondents age 65 and over (Figures 4 and 5). Concern toward adverse reactions was especially prominent among respondents age 65 and over who had not yet received the third shot.
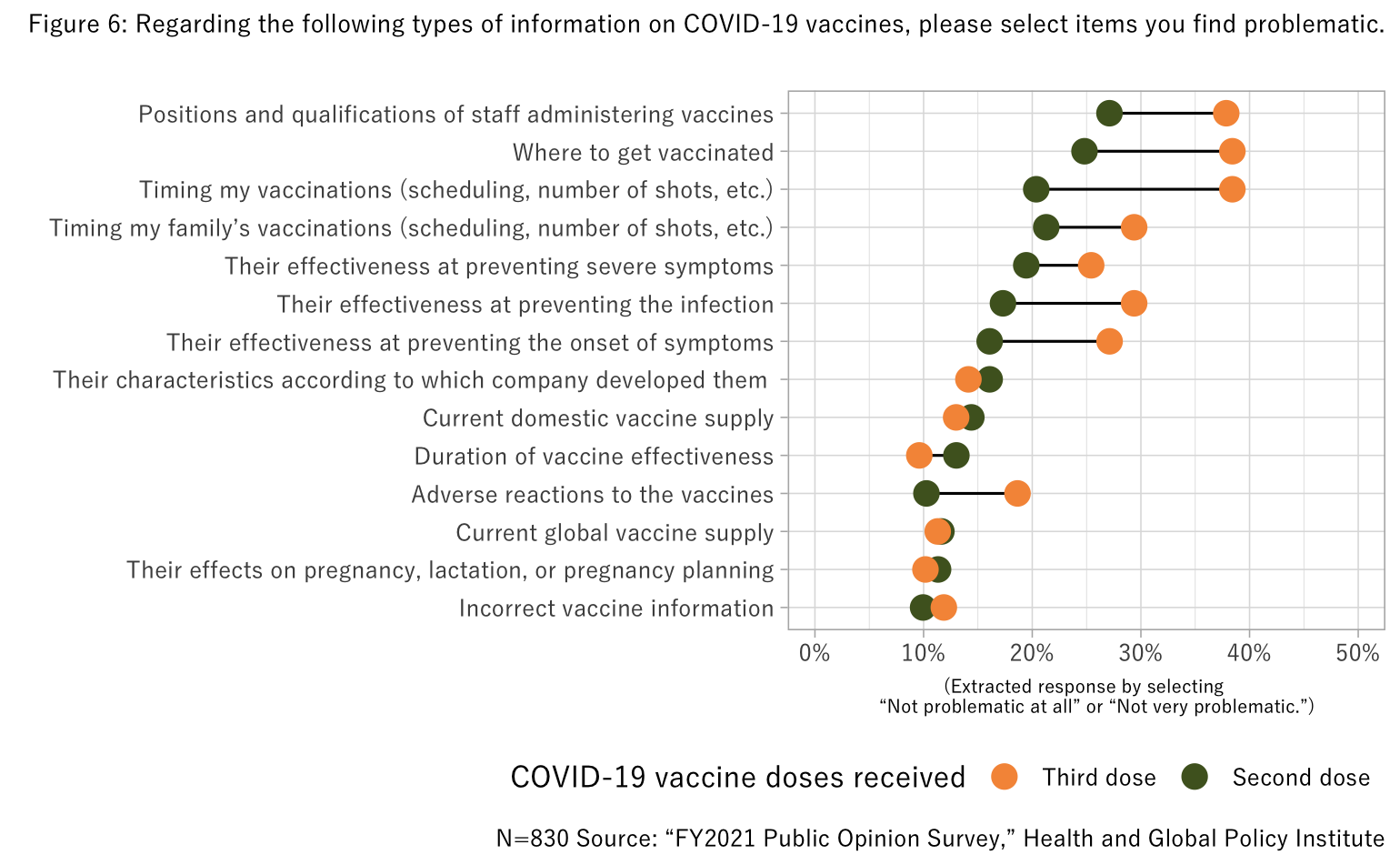
Respondents were asked to rate several statements regarding COVID-19 vaccines on a scale from “Not problematic at all” to “Very problematic.” Comparing the total number of responses that said “Not problematic at all” or “Not very problematic” for each question, we see that those with the third shot found there to be no problems with many statements on the current state of information. Conversely, a high percentage of respondents felt that information on vaccine production and provision systems needs to be studied, discussed, and resolved. These matters included characteristics of the companies that developed the vaccines, domestic supply status, and global supply status. They also included information on post-vaccination effects, such as effects on pregnancy and duration of effectiveness.
Questions on General Immunization and Vaccination Policy Not Limited to COVID-19 Vaccines
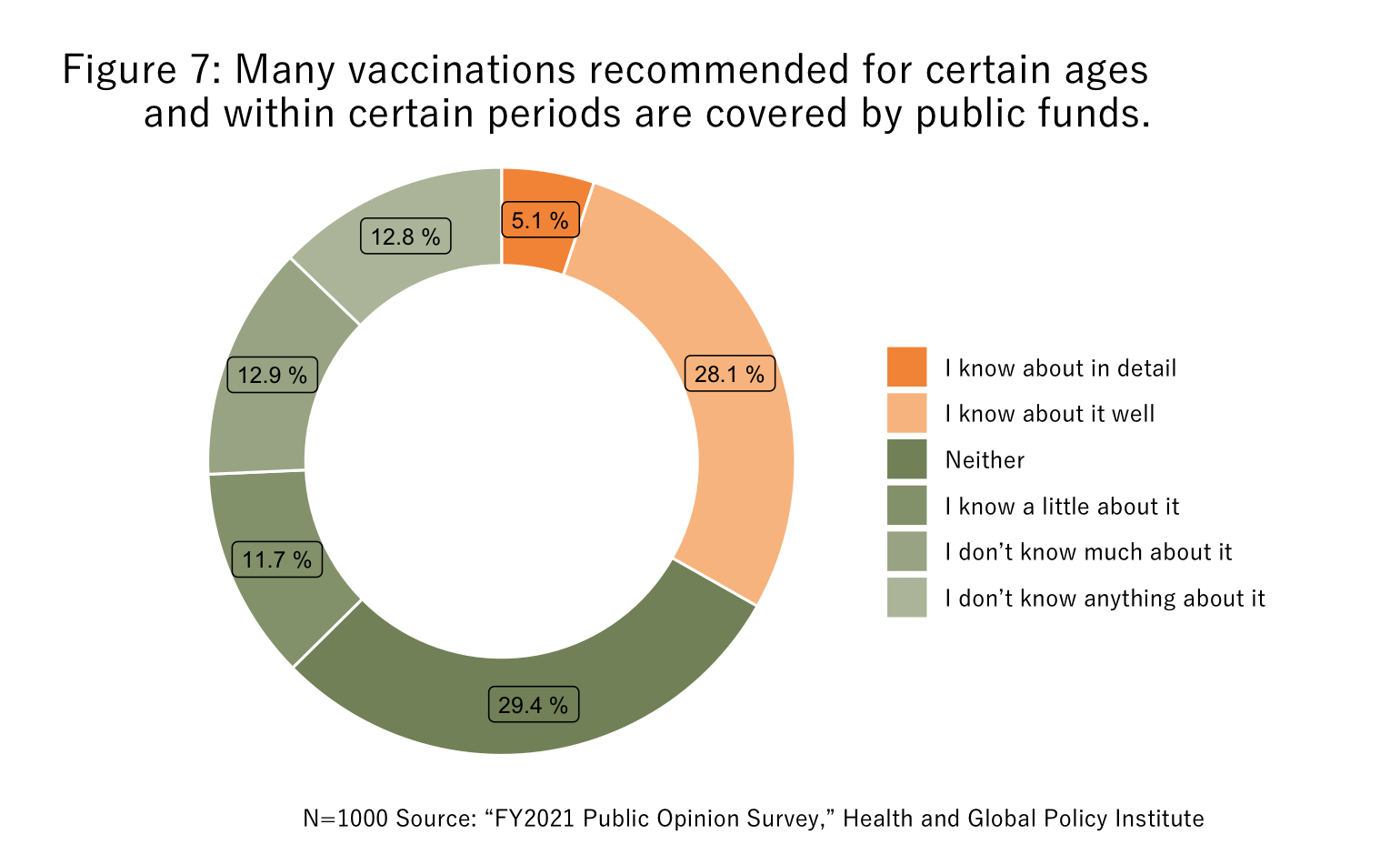
In a question on general immunization and vaccination policy not limited to COVID-19 vaccines, approximately 30% of respondents were aware that vaccinations are conducted with coverage from public funds. Although vaccinations for over 90% of the citizens of Japan are covered by public funds, awareness toward this fact was extremely low (Figure 7).
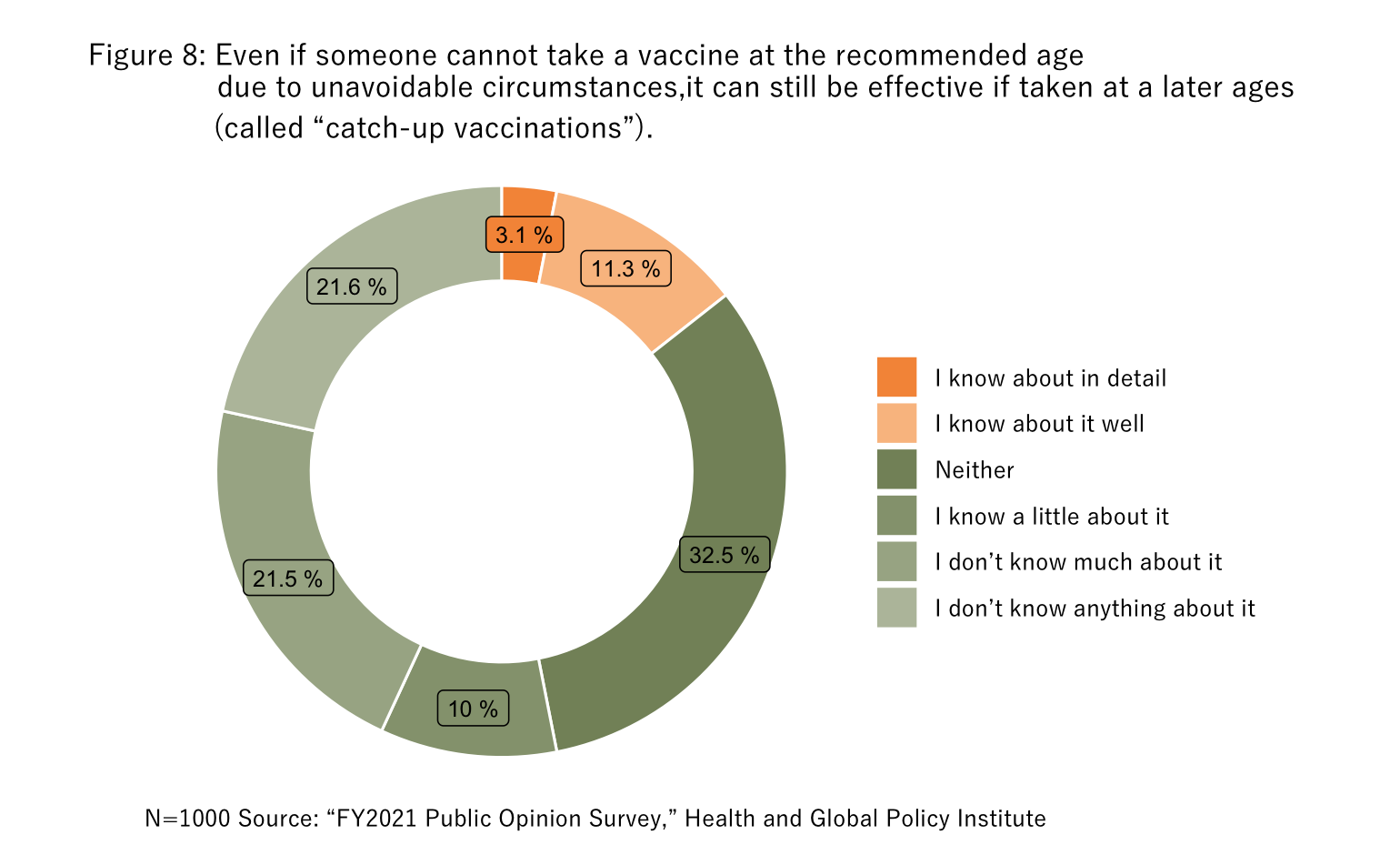
Coverage periods for routine vaccinations are defined by the Immunization Law, and even those outside the targeted age groups can be vaccinated within coverage periods with partial or full public funding. Furthermore, people who have missed vaccinations due to unavoidable reasons such as illnesses requiring long-term treatment are still eligible for routine vaccinations within two years of recovering. However, if that period has already ended, or if someone wants to be vaccinated outside the period of eligibility for personal reasons or other reasons, their vaccination will be treated as voluntary, and they will have to pay the full cost out-of-pocket. Vaccinations provided to make up for delays are called “catch-up vaccinations,” but we found awareness toward the effectiveness of these catch-up vaccinations to be low, at just over 10% (Figure 8).
HGPI is actively working to advance immunization and vaccination policy. For more information about this project, please click here.
Top Research & Recommendations Posts
- [Policy Recommendations] Reshaping Japan’s Immunization Policy for Life Course Coverage and Vaccine Equity: Challenges and Prospects for an Era of Prevention and Health Promotion (April 25, 2025)
- [Research Report] Perceptions, Knowledge, Actions and Perspectives of Healthcare Organizations in Japan in Relation to Climate Change and Health: A Cross-Sectional Study (November 13, 2025)
- [Research Report] The 2025 Public Opinion Survey on Healthcare in Japan (March 17, 2025)
- [Research Report] The 2026 Public Opinion Survey on Healthcare in Japan (February 13, 2026)
- [Research Report] 2019 Survey on Healthcare in Japan
- [Research Report] Building a Mental Health Program for Children and Measuring its Effectiveness (June 16, 2022)
- [Policy Recommendations] Developing a National Health and Climate Strategy for Japan (June 26, 2024)
- [Research Report] The Public Opinion Survey on Child-Rearing in Modern Japan (Final Report) (March 4, 2022)
- [Research Report] The 2023 Public Opinion Survey on Satisfaction in Healthcare in Japan and Healthcare Applications of Generative AI (January 11, 2024)
- [Policy Recommendations] Mental Health Project: Recommendations on Three Issues in the Area of Mental Health (July 4, 2025)
Featured Posts
-
2026-02-27
[Registration Open] (Webinar) The 142nd HGPI Seminar “World Kidney Day 2026” Theme in Focus: The Current State of Green Nephrology and Green Dialysis—Balancing Kidney Health and Planetary Health (March 10, 2026)
![[Registration Open] (Webinar) The 142nd HGPI Seminar “World Kidney Day 2026” Theme in Focus: The Current State of Green Nephrology and Green Dialysis—Balancing Kidney Health and Planetary Health (March 10, 2026)](https://hgpi.org/en/wp-content/uploads/sites/2/The142nd_HGPI_Seminar.jpg)
-
2026-03-03
[Registration Open] Online Seminar “Implementing Chronic Kidney Disease (CKD) Measures into Society: Towards a Data-Driven Health System” (April 21, 2026)
![[Registration Open] Online Seminar “Implementing Chronic Kidney Disease (CKD) Measures into Society: Towards a Data-Driven Health System” (April 21, 2026)](https://hgpi.org/en/wp-content/uploads/sites/2/HGPI_20260421_CKDonlineseminar-.png)