[Research Report] The Public Opinion Survey on Global Health (August 22, 2022)
date : 8/22/2022
Tags: AMR, Global Health, Survey on Healthcare in Japan, Women's Health
![[Research Report] The Public Opinion Survey on Global Health (August 22, 2022)](https://hgpi.org/en/wp-content/uploads/sites/2/gh-survey202208_ENG.jpg)
Health and Global Policy Institute (HGPI) has presented the results of its public opinion survey on global health. It was conducted among 1,000 people in March, 2022, with participants being selected by age, sex, and region in ratios in that correspond to the demographics of Japan’s total population.
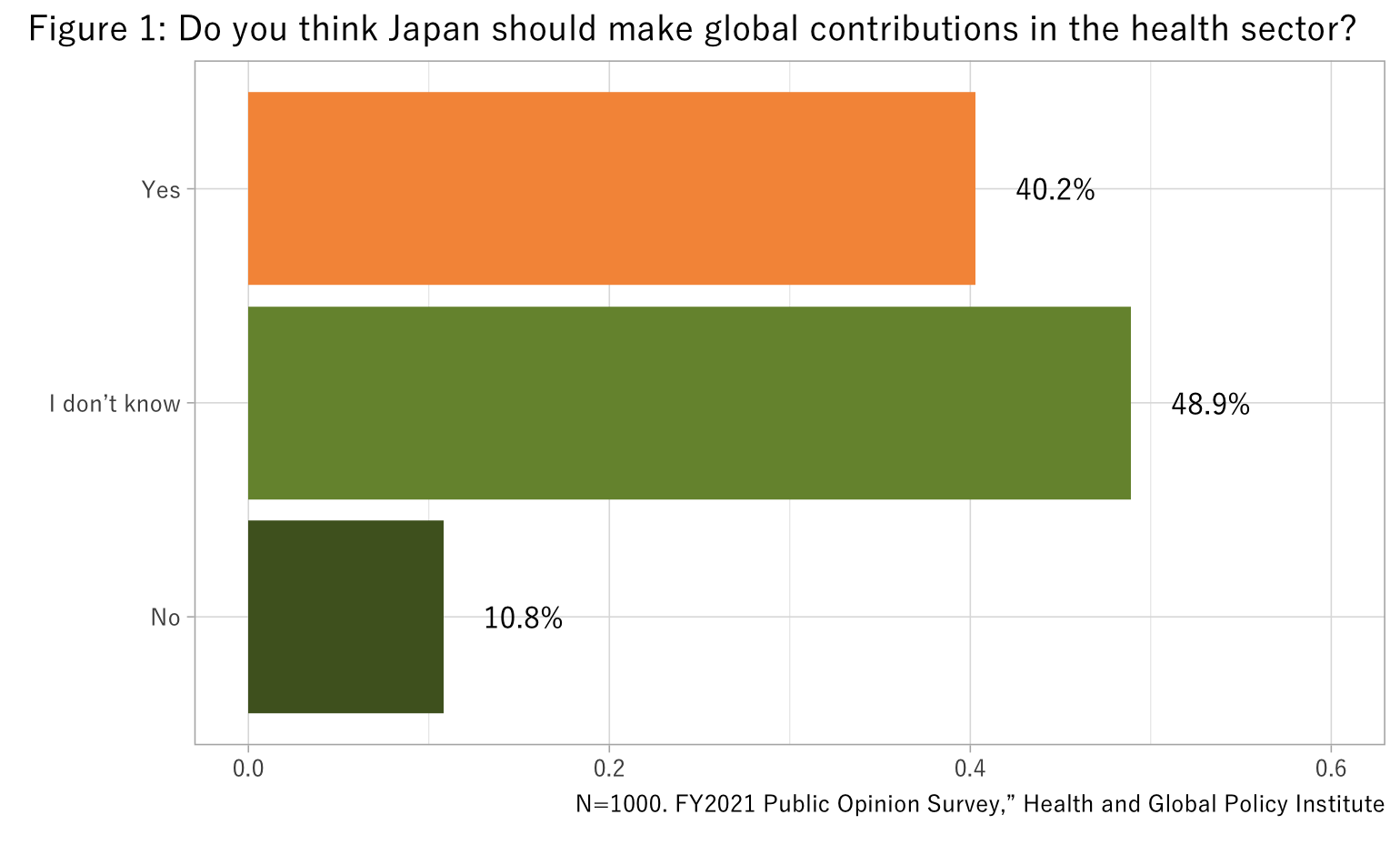
When asked if Japan should make global contributions in the health sector, 40.3% of respondents said that it should (Figure 1).
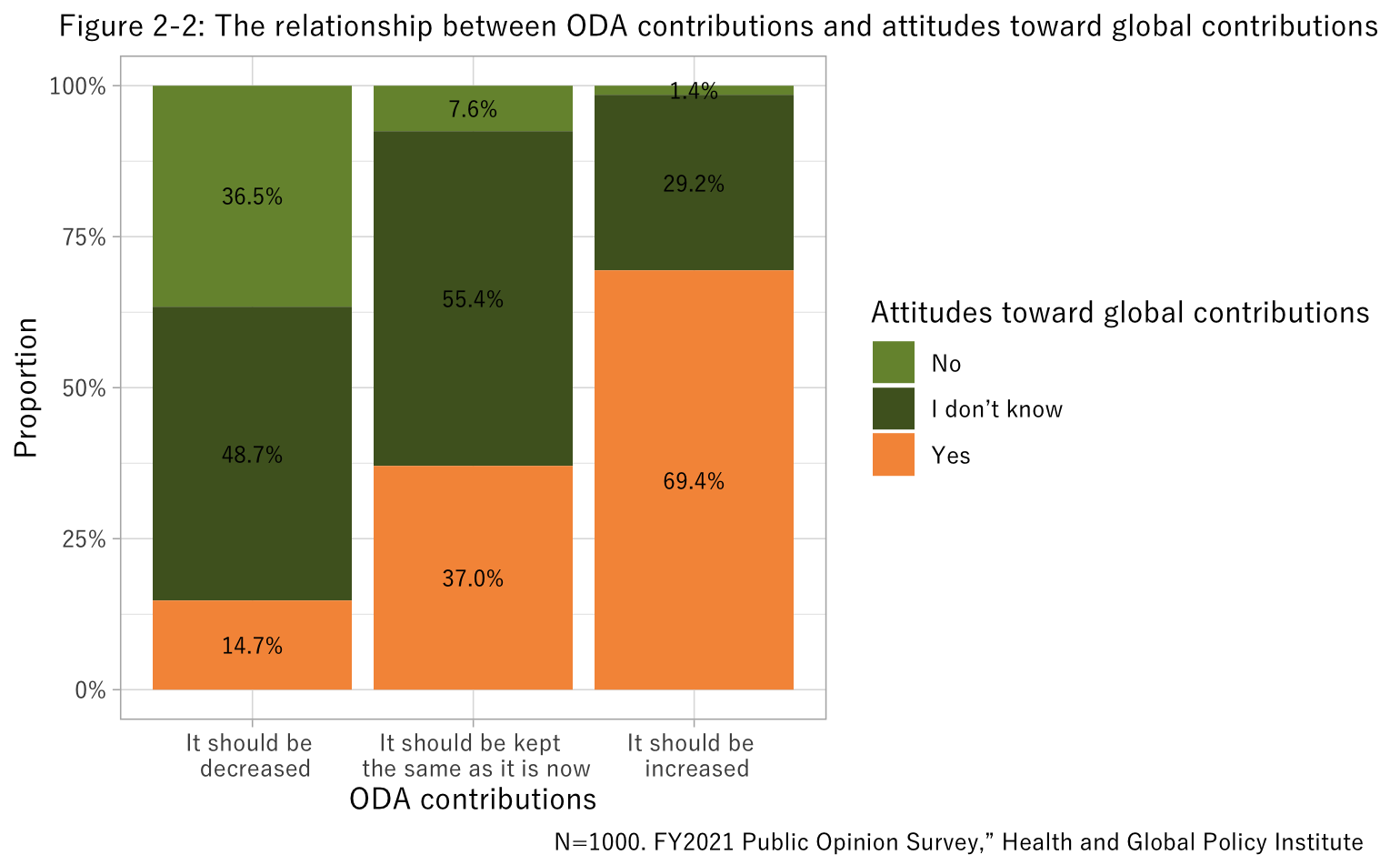
In a question on the per capita financial burden of Japan’s Official Development Assistance (ODA), one method of making global contributions, 20.9% of respondents said it should be increased, even when compared to per capita financial burdens in other Organisation for Economic Co-operation and Development (OECD) members (Figure 2-1). We also found that a higher percentage of those who supported increased per capita financial burden also agreed that Japan should contribute on the global level (Figure 2-2).
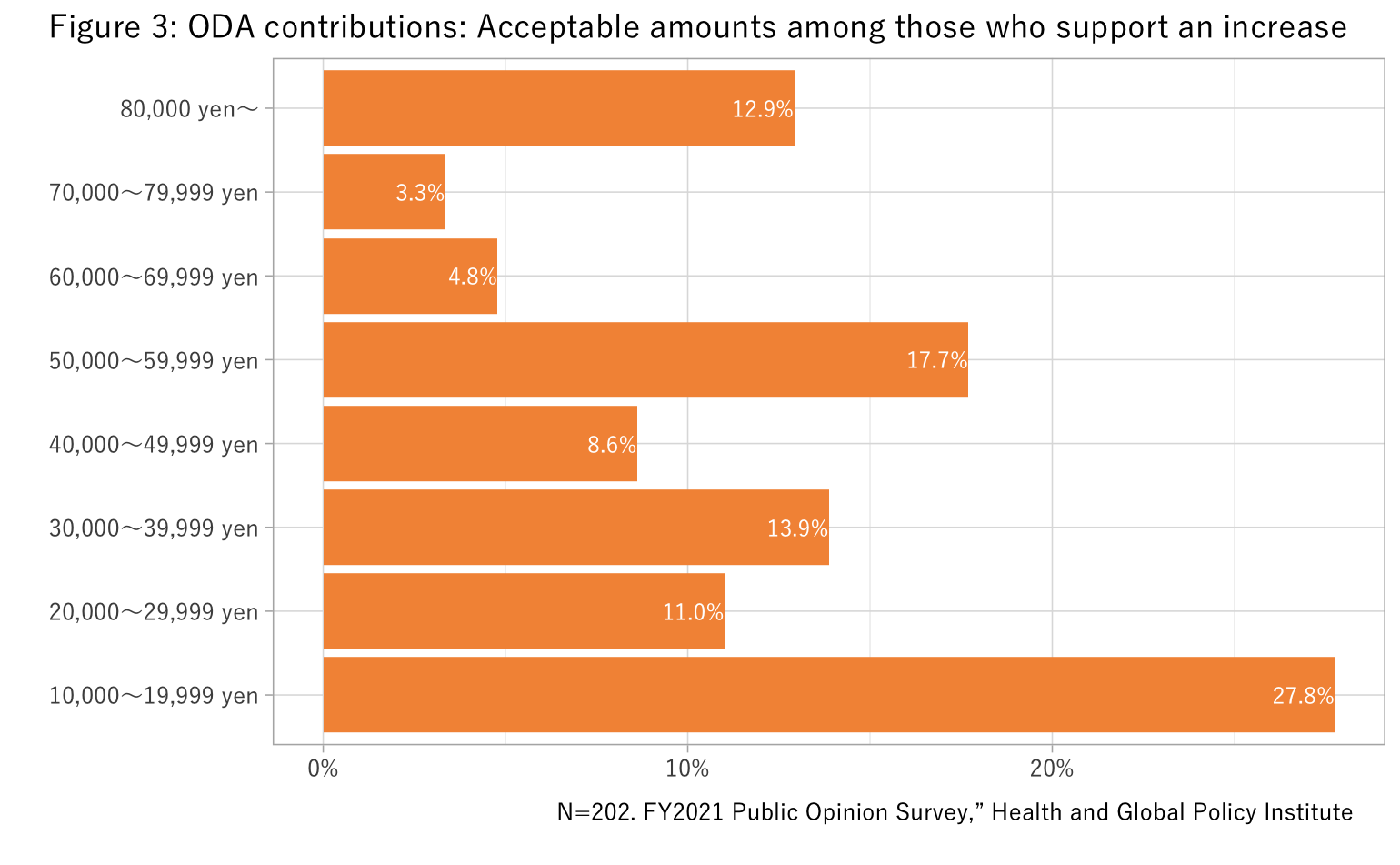
Respondents who thought ODA contributions should be increased were asked what amount would be acceptable to pay. Although many said 10,000 to 19,999 yen, we did not observe a decline in support as proposed ODA contribution increased (Figure 3).
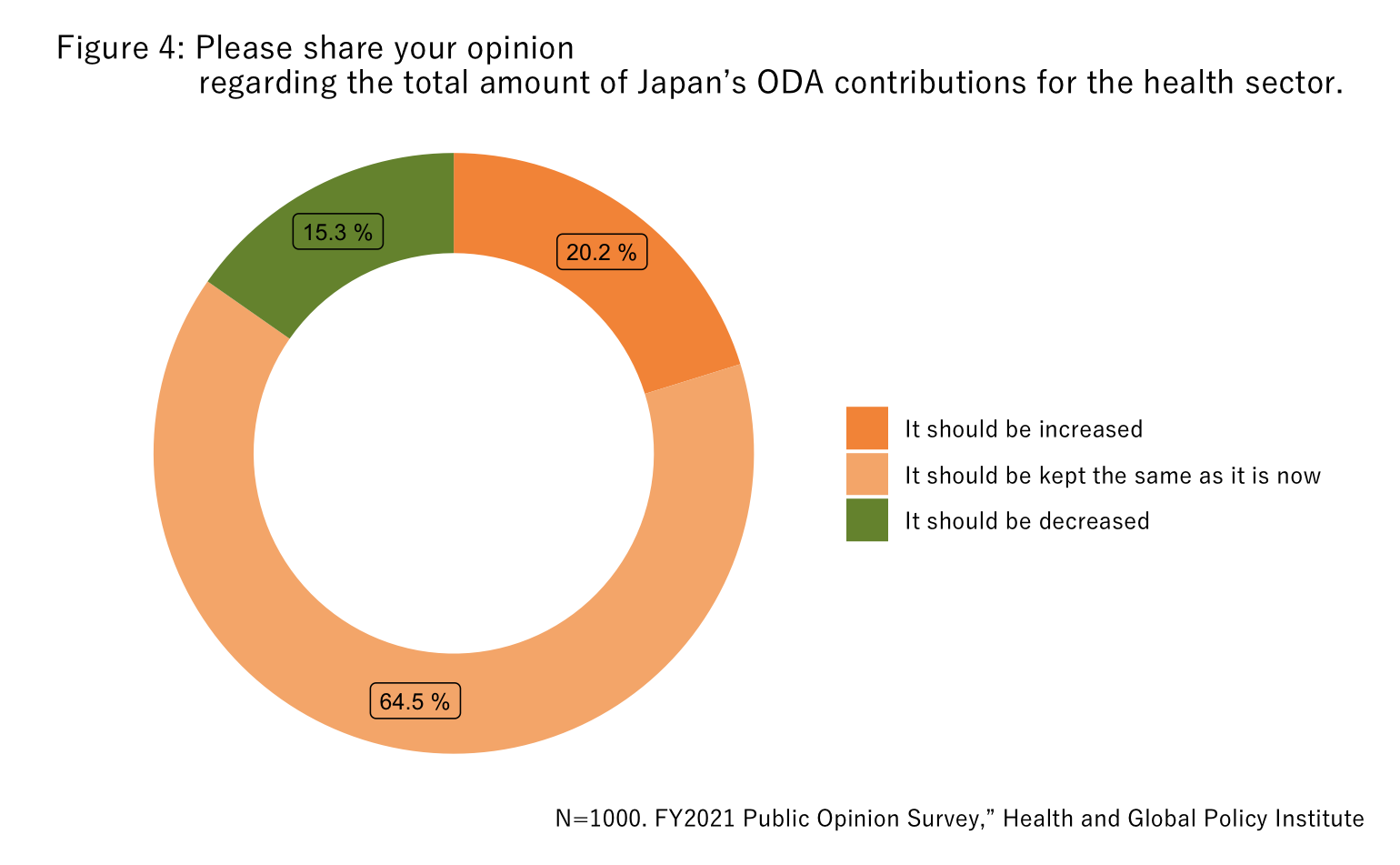
When asked about the proportion of ODA contributions that should be devoted to the health sector, 15.3% selected “It should be kept the same” and 20.4% replied, “It should be increased,” which were similar proportions as the question regarding total ODA contributions (Figure 4).
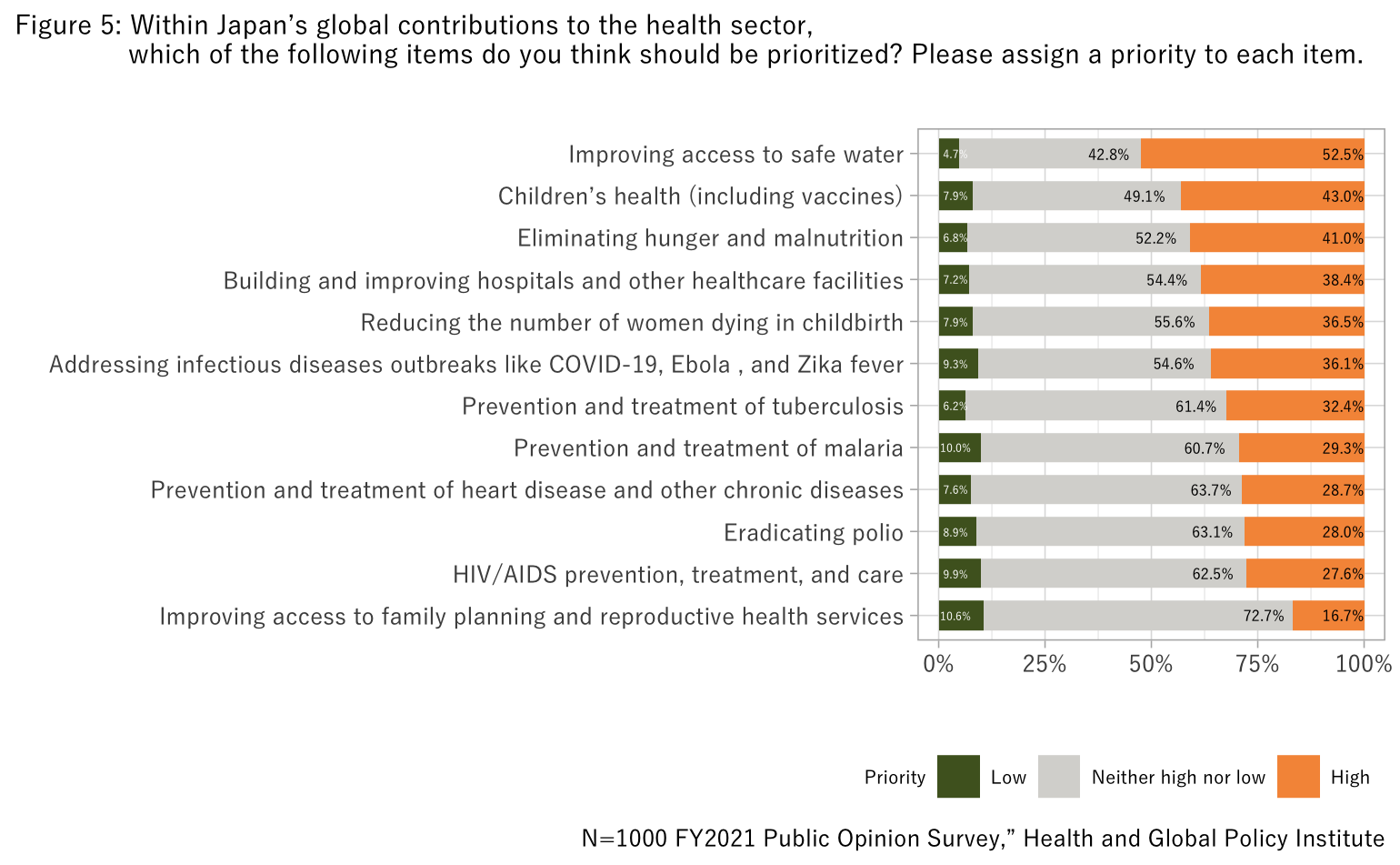
Next, respondents were asked to rank various areas within Japan’s global contributions to the health sector by assigning them either “Low,” “Neither high nor low” or “High” priority. Looking at the results, we see that “Improving access to safe water” was assigned the highest priority, with over half of respondents labeling it as “High.” This was followed by “Children’s health (including vaccinations)” and “Eliminating hunger and malnutrition.” Although “Improving access to family planning and reproductive health services” was assigned relatively low priority, the proportion of respondents who rated it “Low” was similar to other options, while a noticeably larger proportion selected “Neither high nor low” (Figure 5).
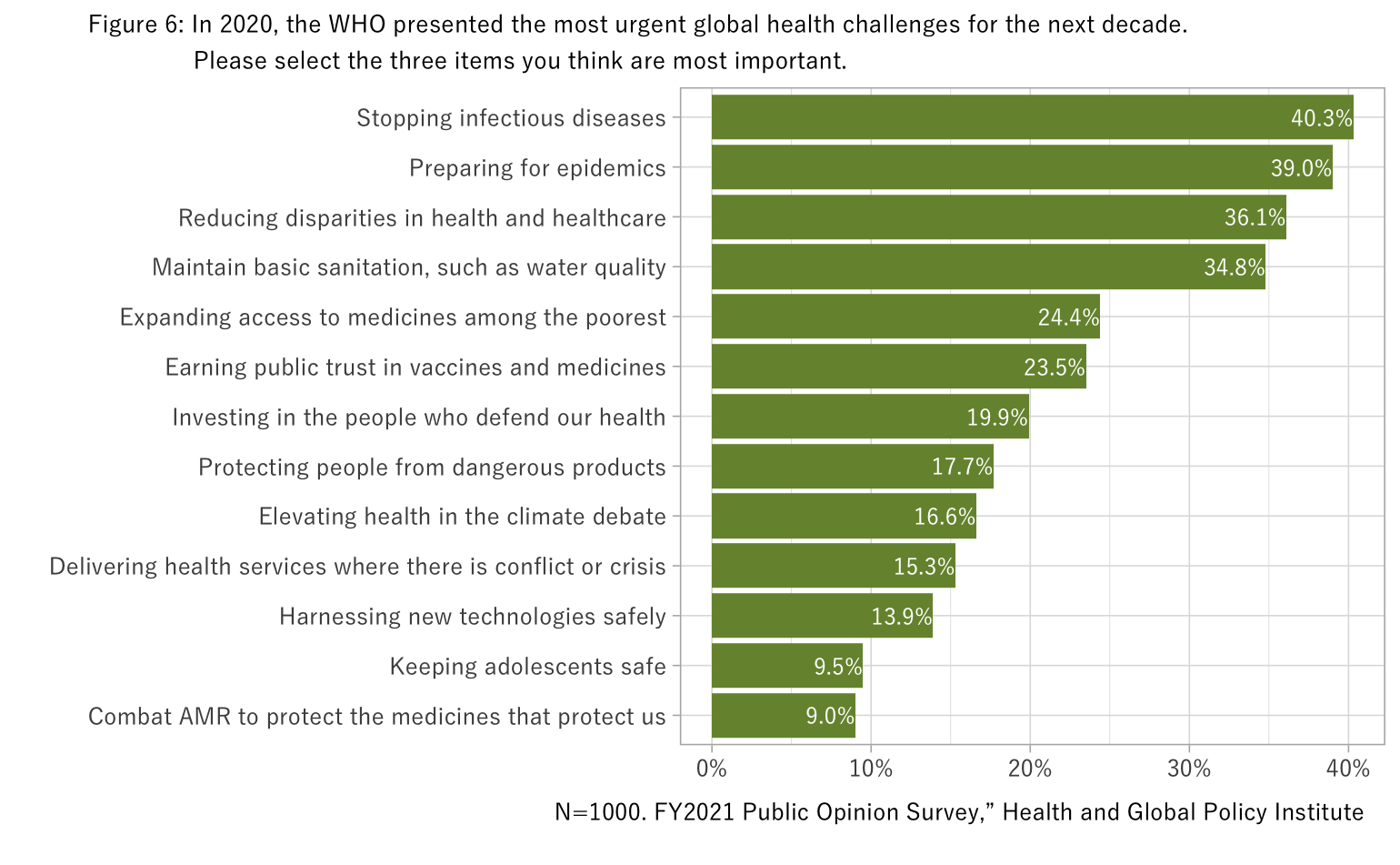
We asked respondents to select the three most important items among the urgent health challenges to address by 2030 identified by the World Health Organization (WHO). Although “Stopping infectious diseases” and “Preparing for epidemics” were assigned the highest priority, which may be a reflection of the impact of the COVID-19 pandemic, there was low awareness toward another topic related to infectious diseases, the need for countermeasures against antimicrobial resistance (AMR), as shown by the low selection rate for “Combat AMR to protect the medicines that protect us.”
HGPI is engaged in broad activities for topics like global health, women’s health, and AMR countermeasures. For details on each of these projects, please see the following.
Top Research & Recommendations Posts
- [Policy Recommendations] Reshaping Japan’s Immunization Policy for Life Course Coverage and Vaccine Equity: Challenges and Prospects for an Era of Prevention and Health Promotion (April 25, 2025)
- [Research Report] Perceptions, Knowledge, Actions and Perspectives of Healthcare Organizations in Japan in Relation to Climate Change and Health: A Cross-Sectional Study (November 13, 2025)
- [Research Report] The 2025 Public Opinion Survey on Healthcare in Japan (March 17, 2025)
- [Research Report] The 2026 Public Opinion Survey on Healthcare in Japan (February 13, 2026)
- [Research Report] 2019 Survey on Healthcare in Japan
- [Research Report] Building a Mental Health Program for Children and Measuring its Effectiveness (June 16, 2022)
- [Policy Recommendations] Developing a National Health and Climate Strategy for Japan (June 26, 2024)
- [Research Report] The Public Opinion Survey on Child-Rearing in Modern Japan (Final Report) (March 4, 2022)
- [Research Report] The 2023 Public Opinion Survey on Satisfaction in Healthcare in Japan and Healthcare Applications of Generative AI (January 11, 2024)
- [Policy Recommendations] Mental Health Project: Recommendations on Three Issues in the Area of Mental Health (July 4, 2025)





![[Registration Open] Online Seminar “Implementing Chronic Kidney Disease (CKD) Measures into Society: Towards a Data-Driven Health System” (April 21, 2026)](https://hgpi.org/en/wp-content/uploads/sites/2/HGPI_20260421_CKDonlineseminar-.png)
